As entrepreneurs you take risks every day, one of those risks should not be tied to making a wrong decision on your entity structure. In this Part 3, we'll discuss how properly structuring your business can significantly decrease risks and increase the net value of your business. As an entrepreneur, one of the first questions that you are faced with is what kind of entity you should form. The possibilities are seemingly endless. You can go with a C-Corp, an S-Corp, an LLC, or an S-LLC. Let's explore the Pros and Cons of each type which may help you get some clarity for a decision that is not always a one-size-fits-all determination.
Pros and Cons of the Different Entity Types
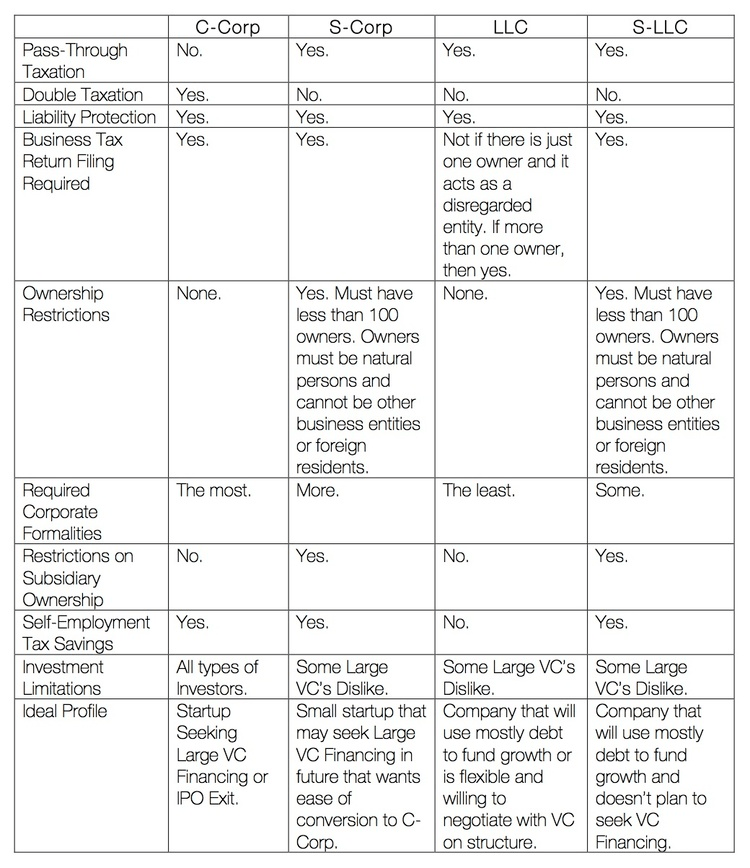
C-Corp:
- Pros. The advantages of a C-Corp are the flexibility of capital structure and its attractiveness to all types of investments, both VC and debt financing. Originally issued stock in C-Corps qualify as Qualified Small Business Stock, which can result in some capital gains savings.
- Cons. The cons of the C-Corp are its double taxation. This is not a big deal when the company is generating losses, but at the time of an exit, a founder can lose serious money. Another con of C-Corps is that there are many corporate formalities requiring compliance to maintain the liability protections of the C-Corp.
- Ideal Candidate. High-growth startups wanting to attract top national VC firms or whose exit plan is through an IPO.
S-Corp:
- Pros. The pros of an S-Corp are the avoidance of double taxation as well as the ability to lessen employment and FICA taxes on owner-employees.
- Cons. The cons of the S-Corp are that it is extremely limited in its capital structure. For example, all shareholders must be individuals with a few limited exceptions for grantor trusts, and there can only be one class of financial ownership interests, which means no preferred stock. Both of these are issues that will not allow for VC financing. An additional con of S-Corps is that many corporate formalities need to be complied with to maintain the liability protections of the S-Corp. If you slip up, that slip up could result in a technical termination of the entity which could result in some pretty steep tax liabilities.
- Ideal Candidate. Small consulting or service businesses with individual owners who don’t plan on raising Venture Capital or Private Equity financing.
LLC:
- Pros. The pros of the LLC are numerous: (1) pass-through taxation; (2) flexibility in capital structure; (3) attractiveness to vast majority of potential investors; and (4) flexibility in management and lack of entity formalities.
- Cons. Disfavored by some VC investors, but with proper planning as discussed below, the adverse tax consequences can be mitigated. It doesn’t have the ability to minimize FICA taxes to owner-employees as all income is passed through to its owners.
- Ideal Candidate . LLCs are the preferred entity because they are well suited for most businesses unless your planned exit is an IPO.
S-LLC:
- Pros. The pros of the S-LLC are all of the benefits of LLC with the addition of being able to minimize FICA taxes.
- Cons. All of the disadvantages of S-Corps except the rigid corporate formalities are lessened.
- Ideal Candidate. Same as for S-Corps, but these entities are a little more flexible in entity formalities and are thus generally more favorable than S-Corps.
The following table compares the above-listed entity types:
Conclusion As you can see this is a complex decision to make and one that you should discuss carefully with both your attorney and accountant and preferably at the same time. The three takeaways from this article are the following:
- Entity structuring is not a one-size-fits-all scenario and needs to take into account many factors, including the type of business involved, its owners, and how it plans on raising money in the future. Each entity comes with its own risks.
- LLCs are oftentimes the best entity structure for entrepreneurs.
- Hire good corporate counsel early to help you take the right risks, and the few thousand dollars you spend on them could save you mountains of money at exit.




